Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting the body’s ability to process glucose effectively, has emerged as a global health concern. Since more and more people are getting it, it’s really important to learn a lot more about how it works, how to handle it, and how to stop it from happening.

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterised by elevated blood sugar levels due to either insufficient insulin production, ineffective use of insulin, or both. There are primarily three types:
1. Type 1 Diabetes: Typically diagnosed in children and young adults, this results from the body’s failure to produce insulin due to an autoimmune reaction.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, often associated with lifestyle factors like obesity and sedentary habits. In type 2 diabetes, the body doesn’t use insulin properly, leading to insulin resistance.
3. Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy when blood sugar levels rise above normal levels. If unmanaged, it can pose risks to both the mother and baby.
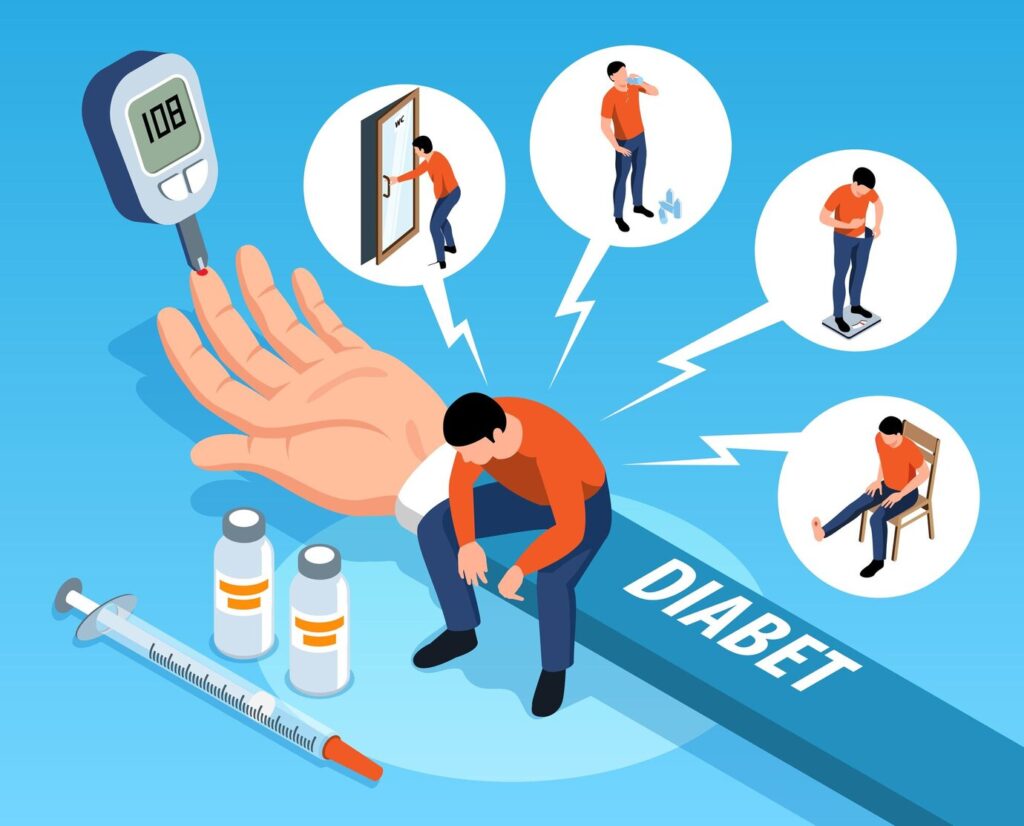
Signs and Symptoms
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue and irritability
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet

Management Strategies
1. Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sugar and refined carbohydrates intake.
2. Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Exercise helps control blood sugar levels and improves overall health.
3. Medication and Insulin Therapy: Type 1 diabetes often requires insulin injections. Type 2 diabetes may be managed with oral medications, insulin, or other injectables.
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels as advised by a healthcare professional to track how well the treatment plan is working.
5. Stress Management and Mental Health Support: Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so adopting stress-reduction techniques is essential. Additionally, mental health support can help cope with the emotional aspects of living with diabetes.

Preventive Measures
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Regularly screen for diabetes if you have risk factors like obesity, family history, or a sedentary lifestyle.
- Stay informed about diabetes management and seek medical advice promptly.
Interviews with Experts
Over the past two decades, I’ve had the privilege of interviewing leading experts in the field of diabetes, including researchers, endocrinologists, and healthcare professionals. Their insights have shed light on innovative treatments, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing research aimed at improving diabetes care and management.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management and prevention. With the right lifestyle choices, regular medical care, and a supportive environment, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite living with diabetes.
Remember, managing diabetes involves a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and individuals affected by the condition. Stay informed, stay active, and prioritise your health to minimise the impact of diabetes on your life.

